Force spectroscopic detection of peptide cleavage by thrombin exploiting biotin–streptavidin interactions in a bio-sensing context†
Abstract
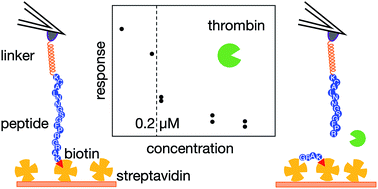
Atomic-force-microscopy-based single-molecule force spectroscopy (AFM-SMFS) has become an important technique as the basis of novel, label-free biosensing strategies. In this work, we explored the possibility of using AFM-SMFS to detect the specific peptide cleavage activity by thrombin proteases. To achieve this aim, an oligopeptide with a sequence that is recognized and cleaved by thrombin was spanned between an AFM tip and a solid surface via a PEG-based linker system including the stable biotin–streptavidin receptor/ligand complex. We found that force spectral signatures associated with the biotin–streptavidin unbinding in the absence of thrombin can be clearly distinguished from the signatures of spectra collected after thrombin-induced peptide cleavage. However, this is possible only in a well-defined window of peak force and tip–sample separation distance values, in which specific streptavidin–biotin interactions do not overlap with non-specific interactions among all the other system components. The results were employed to engineer a sensing architecture capable of detecting the presence of thrombin at concentrations higher than about 0.2 μM.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...