A sensitive and quantitative immunochromatographic assay for HBsAg based on novel red silica nanoparticles†
Abstract
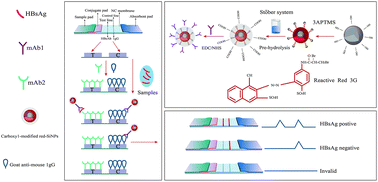
An immunochromatographic assay (ICA) based on red silica nanoparticles (red-SiNPs) was developed for quantitative detection of hepatitis B surface antigen (HBsAg) in serum. Red SiNPs have unique optical properties and remarkable stability compared to red latex microspheres. Red-SiNPs functionalized with anti-HBsAg mAb1 were employed as detection immuno-probes. The sandwich-type immunoreaction structures were formed on ICA strips, and the accumulation of red SiNPs-mAb1 on the test line produced characteristic red color bands, enabling visual detection of HBsAg without instrumentation. Quantitative detection was performed by researching the relationship between the HBsAg concentration and the corresponding peak area of the gray value of the test line with a camera and image analysis software Image J. Under optimal conditions, the visual limit of detection (vLOD) of the strip for the qualitative detection of HBsAg is 1 ng mL−1, which is lower than that of the routinely used red latex microsphere-based ICA. In the quantitative detection, the peak area of the gray value of the test line and the HBsAg concentration show a good linearity when the HBsAg concentration is in the range of 5–500 ng mL−1. The calibration equation was y = 370.6118 + 9.6673x (R2 = 0.9962) and the limit of detection (LOD) of the method was 0.97 ng mL−1 (S/N = 3). Our proposed method provides promising and versatile opportunities for the rapid and quantitative screening of other proteins at relatively sensitive levels by combining a colored label with ICA.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Analytical Methods Recent HOT articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...