A new boronate-affinity hollow solid phase extraction adsorbent for the enrichment of cis-diol-containing isoflavones in soybean milk samples
Abstract
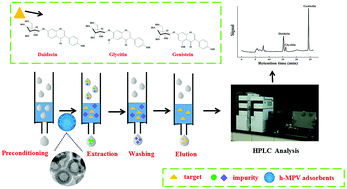
In this study, a new boronate-affinity hollow adsorbent was successfully fabricated. This adsorbent was prepared using mesoporous MCM-48 as a sacrificial support, methacrylic acid (MAA), N,N-methylenebisacrylamide (MBA) and azobisisobutyronitrile (AIBN) were applied as a functional monomer, cross-linker and initiator, respectively, and further modified with boronic acid groups (4-vinylphenylboronic acid, VPBA) to improve the enrichment efficiency. Such materials were composed of a hollow structure, a hydrophilic polymer coating of poly(MBA-MAA), and a VPBA-functionalized shell designed for capturing isoflavones. The resulting material coupled with high-performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) was applied to analyze three cis-diol isoflavones (daidzin, glycitin, and genistin) in soybean milk samples. The sorbent was characterized by transmission electron microscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectrometry and thermo-gravimetric analysis. Several parameters affecting the extraction efficiency were optimized. Owing to the hollow structure, more binding sites were located on the inner and outer surfaces of this material, which could facilitate the binding of the target molecules to the adsorbent. Adsorption selectivity studies indicated that the prepared material can selectively recognize isoflavones. Under optimized conditions, the limits of detection of the method were 3.8 to 7.3 μg L−1 for the three isoflavones based on a signal-to-noise ratio of 3 : 1. The spiked recoveries were found to be between 67.4 and 104.7% (the relative standard deviations were less than 3.8%, n = 3). This indicated the superiority of the method in selective extraction of isoflavones even from complex matrices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...