Novel fluorescent probe with a bridged Si–O–Si bond for the reversible detection of hypochlorous acid and biothiol amino acids in live cells and zebrafish†
Abstract
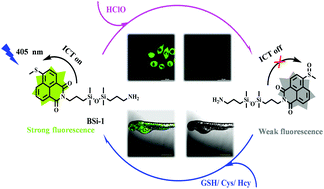
Herein, we report the design of a novel fluorescent probe consisting of a naphthalimide fluorophore and a silicone small molecule for the reversible detection of hypochlorous acid and biothiol amino acids. The response mechanism of BSi-1 is based on the concept of the S-based oxidation/reduction. The probe was found to be suitable for imaging HOCl in HeLa, RAW 264.7 cells and zebrafish, demonstrating its utility in biological applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...