Comparison between conventional and frit-inlet channels in separation of biopolymers by asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation
Abstract
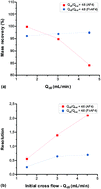
Asymmetric flow field-flow fractionation (AF4) is a separation technique in which a focusing/relaxation step is used after the sample is injected onto the separation channel. During the focusing/relaxation step, the sample is focused by two counter-directed flows. This allows sample components to establish a diffusion-dependent equilibrium concentration profile. The focusing step may, in some cases, cause a loss of sample due to adsorption into the accumulation wall (i.e. the membrane) or due to aggregation of the sample. In addition, the increase in sample concentration during the focusing step may prevent complete relaxation and cause overloading effects. In this study, a modified AF4 channel equipped with a frit inlet (FI-AF4) is utilized, where the sample is relaxed hydrodynamically as it enters to the channel through the frit. The main advantage of the FI-AF4 channel is to omit the focusing step. The FI-AF4 channel could also allow higher injection mass than in a conventional channel while still avoiding overloading. The purpose of the present study is to compare two channels (conventional and FI-AF4 channels) in terms of the plate height (H), resolution (Rs) and the mass recovery for analysis of a mixture of glycogen and pullulan. In addition, waxy maize (WM) starch was used to compare the mass overloading of the two channels. The results show that the type of relaxation method (i.e. focusing or hydrodynamic relaxation) had no significant effect on mass recovery. The resolution (Rs), was higher in the conventional AF4 channel than in the FI-AF4 channel for the separation of glycogen and pullulan. The results also show that it was possible to inject a higher mass of WM starch (i.e. twice the mass) onto the FI-AF4 channel, compared to a conventional AF4 channel, without observing an overloading effect.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...