A pH-based sensor array for the detection and identification of proteins using CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as an indicator†
Abstract
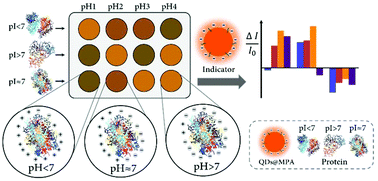
Protein identification is very important in the field of clinical medicine and diagnosis. Here, we report a novel and simple sensor array for the detection and identification of proteins using pH buffer solutions as sensing elements. Different proteins in various pH solutions have different net surface charges including positive, negative or no charge. Such differences may allow a pattern recognition-based sensor array for protein identification. When using negatively charged CdSe/ZnS quantum dots as an indicator, the interactions between a charged protein and quantum dots result in fluorescence changes, generating a differential response pattern for the protein. The result shows that proteins with pI > 7, pI = 7 or pI < 7 can be differentiated successfully. Moreover, complex protein mixtures are also able to be identified and the results demonstrate that surface charge may play an important role in protein sensing. The HSA of different concentrations in water and human urine can also be detected by using the sensor array. It is demonstrated that the proposed sensor array has potential applications in clinical diagnosis and proteomics.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...