Highly sensitive, stretchable and wearable strain sensors using fragmented conductive cotton fabric†
Abstract
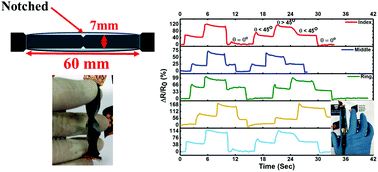
Recent advancements in stretchable, flexible and wearable strain sensors, based on natural materials, show their interesting potential for use in human motion detection, soft robotics and human–machine interactions. However, a grand challenge still exists: finding an effective strain-sensing mechanism to obtain both high stretchability and high sensitivity through a facile manufacturing technique. In this paper, a simple, environmentally friendly, and scalable process to develop such strain sensors based on cotton fabric, which is an abundant, cost-effective and lightweight natural material, is discussed. An effective coating technique is proposed to achieve highly conductive cotton fabric with the aid of a conductive ink that is a hybrid of graphene nanoplatelets and carbon black particles. The sandwich-structured wearable strain sensors can work within a wide strain range of up to 400%, with an ultrahigh maximum gauge factor of 102 351, caused by the formation of controlled intentional cracks within the fabric after rupture training. The strain sensors show great performance at very low strain levels (less than 2%). Their excellent response in detecting a full range of human movement is also demonstrated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...