Influence of Cu and Na incorporation on the thermodynamic stability and electronic properties of β-In2S3
Abstract
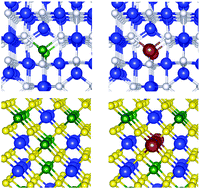
The aim of this study is to understand the effect of Na and Cu incorporation in In2S3, which is representing a Cd-free buffer system for chalcopyrite-type thin film solar cells based on Cu(In,Ga)Se2 (CIGS). The formation energies and charge states of sodium and copper dopants in In2S3 are investigated by means of calculations based on electronic hybrid density functional theory using supercells of 320-atoms. Our results reveal a negative formation enthalpy of sodium in both In-rich and S-rich samples, which indicates the occurrence of side reactions and explains the existence of a chemically modified buffer layer in the presence of a Na-reservoir. Copper, in contrast, can be incorporated in large concentrations in In-rich In2S3 under n-type conditions, acting as an acceptor and thus limiting the n-type conductivity. For lower Fermi energies, however, reactions between Cu and the buffer material lead to the formation of Cu-containing secondary phases in the buffer side which is in qualitative agreement with experimental observations of Bär et al. [Bär et al., Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2016, 8, 2120]. Sulfur rich samples are found to be more heavily doped under n-type conditions and we expect to have Na- and Cu-containing secondary phases formed under metal-poor growth conditions.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...