Structural construction and photoluminescence tuning via energy transfer in apatite-type solid-state phosphors
Abstract
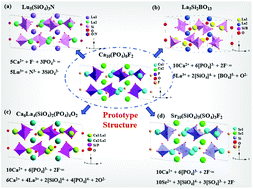
Apatite-type solid-state phosphors have received considerable attention for their versatile chemical compositions in flexible crystal structures as well as the different crystallographic sites for the single doped or codoped activators. For these reasons, these phosphor materials have demonstrated potential applications in different fields, including the solid-state lighting and display industry. Herein, the recent developments in the structural design and photoluminescence tuning of the apatite-type phosphors have been reviewed. First, we summarized the design principles of the crystal chemistry and the discovery of typical apatite-type phosphors, which can also form a variety of multi-component apatite phase compounds from such a mineral model. Second, we described the development of multi-color apatite-type phosphors originating from different doping ion couples and their corresponding energy transfer (ET) process, which in turn can tune the emission colors of phosphors and even realize the single-component white light-emitting emission. Accordingly, this review will promote research on the discovery of new apatite-type phosphors and the photoluminescence tuning strategy via the codoped activators and the related ET behaviour.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Recent Review Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...