Bionic cartilage acellular matrix microspheres as a scaffold for engineering cartilage†
Abstract
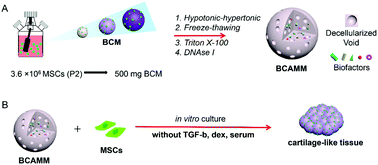
Extracellular matrix (ECM) scaffolds made from decellularized natural cartilage have been successfully used in cartilage lesion repair, but allogeneic cartilage donors are always in shortage and xenogeneic cartilage tissues may have the risk of unknown disease transfer. In this study, we constructed artificial bionic cartilage microspheres by encapsulating MSCs in collagen microspheres and cultured in a chondrogenic-inducing medium. Then, acellular matrix microsphere (BCAMM) scaffolds were fabricated from the cultured microspheres at three different developmental stages. A novel technique was introduced to fabricate BCAMM scaffolds, which enabled the production and utilization of the scaffolds in a short time. Due to the differences in surface morphologies and biological compositions, the three BCAMM scaffolds showed different chondrogenic effects. The 10-day BCAMM (10-BCAMM) scaffold showed the best overall results, successfully inducing MSC chondrogenesis without any additional fetal bovine serum or induction components (TGF-β or dexamethasone). In comparison, the 5-day BCAMM (5-BCAMM) scaffold showed potential osteogenic effects. The advantages of micron-sized BCAMMs are outlined, specifically in the easier decellularization process without grinding, homogeneous cell seeding and infiltration, chondrogenic induction and better fitting to the irregular lesion shape.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...