Lithium-containing biomaterials inhibit osteoclastogenesis of macrophages in vitro and osteolysis in vivo
Abstract
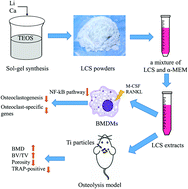
Osteolysis, which is caused by aging, neoplasia, infection, or trauma, is a type of intractable systemic or local syndrome of bone destruction (e.g., peri-implant osteolysis (PIO)). The activation of osteoclasts differentiated from macrophages plays a decisive role in such diseases. To conquer this challenge, herein, a biomaterial capable of inhibiting osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis was designed. Recent research has shown that lithium (Li) can inhibit pro-inflammatory cytokine release in vitro via affecting the pharmacotherapy of psychiatric illnesses. Therefore, we synthesized a pure-phase lithium–calcium–silicate (Li2Ca2Si2O7, LCS) bioceramic and further prepared extracts to assess the effect of LCS on RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis in vitro and Ti particle-induced osteolysis in vivo as well as the corresponding mechanism. The results demonstrated that LCS inhibited RANKL-induced osteoclastogenesis of macrophages, bone resorption area, and F-actin ring formation in a dose-dependent manner. The mechanism is related to the suppression of the NF-kB signaling pathways mediating the inhibitory effects of LCS. Moreover, LCS was found to be able to inhibit calvarial osteolysis in a mouse model through micro-CT and histological analysis. These findings suggest that LCS may be a promising biomaterial for suppressing osteolysis, thus paving the way for the treatment of osteoporosis using bioactive inorganic materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...