Platelets and their biomimetics for regenerative medicine and cancer therapies
Abstract
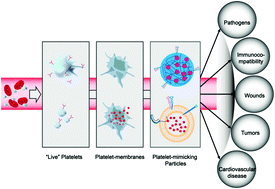
Platelets, circulating blood cells derived from megakaryocytes, play a key role in various physical activities, including coagulation, hemostasis, the body's innate immune response, and cancer metastasis. By taking advantage of their key traits, researchers have developed strategies to exploit platelets and platelet-mimicking nanoassemblies to treat a number of conditions, including wounds, cancers, and bacterial infections. Compared to traditional polymer, liposome, and inorganic nanoparticle-based delivery systems, platelets and platelet-mimicking vehicles hold many advantages. Among these are their enhanced circulation time, their large volumes and surface areas for drug loading or conjugation, and their inherent ability to target some diseases. In this review, we will highlight the recent progress made in the development of disease-targeting platelets and platelet-mimicking vehicles as therapeutic platforms.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...