Bilayer hydrogel mixed composites that respond to multiple stimuli for environmental sensing and underwater actuation†
Abstract
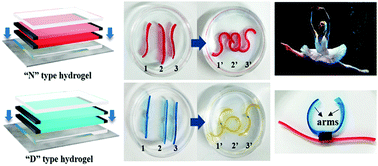
Bilayer-type hydrogel composites that respond to multiple stimuli provide a useful approach for manufacturing soft actuators and intelligent sensors. In this study, we propose two types of bilayer hydrogel composites (referred to as “N” type and “D” type). The “N” type and the “D” type separately consist of poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) (PNIPAM) and poly(2-(dimethylamino)ethyl methacrylate) (PDMAEMA) bilayer hydrogels, with acrylamide (AM) as the co-monomer. The “N” type hydrogel composite exhibits oriented bending as temperature increases or as environmental salt concentration increases. The “D” type also presents oriented bending as temperature increases. Additionally, it demonstrates bending and changes color based on the pH of the surrounding solution, since it is doped with an acid-based pH-indicator. In a demonstration, we present several straight rods composed of a mixture of “N” and “D” type hydrogel composites that are able to morph into the letters “SOS” under environmental changes (temperature or pH). This can be used as a visual environmental indicator, or as an alarm. Furthermore, we show structures composed of a mixture of “N” and “D” composites imitating the flexible motions of a ballet dancer or a Tai Chi master. These mixed bilayer polymer composites may be used for applications in soft robotics, biomimetic devices, and environmental sensors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...