Composites based on heparin and MIL-101(Fe): the drug releasing depot for anticoagulant therapy and advanced medical nanofabrication†
Abstract
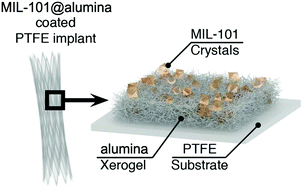
We describe the synthesis and properties of a new composite material based on heparin and MIL-101(Fe) metal–organic framework. The intrinsic instability of MIL-101(Fe) towards hydrolysis enables binding of heparin molecules to the framework structure as is evidenced by DFT calculations and adsorption experiments. The de novo formed heparin–MOF composites showed good biocompatibility in in vitro and demonstrated pronounced anticoagulant activity. The specific interaction between the bioactive molecule and the carrier is critical for the selective degradation of the complex in the body fluids and for the enhanced activity. Hep_MIL-101(Fe) composite could serve as a drug-releasing depot for nanofabrication and to introduce anticoagulant activity to medical devices and biocoatings. Addition of Hep_MIL-101(Fe) to a sol–gel derived thrombolytic matrix allowed the combination of anticoagulant and thrombolytic activities in a single hybrid nanomaterial that could be applied as a bioactive nanocoating for PTFE vein implants.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...