Probing the Qi of traditional Chinese herbal medicines by the biological synthesis of nano-Au†
Abstract
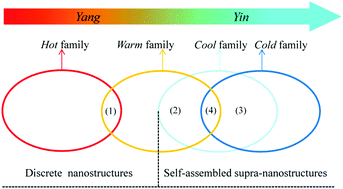
Herbal medicines with different Qi properties (the primary proxy of their therapeutic effects) are used in traditional Chinese medicine to maintain the harmony of vital forces in a human body. In the Western medicinal practice, the classification of Qi into four major families (“Si Qi” in Chinese Pinyin) is a challenging endeavor, especially by a simple non-reductionist approach. The method presented here is however able to distinguish the Qi of herbal medicines based on the measurements of several Qi-related features in a biological synthesis of nano-Au in herbal extracts: solution color, surface plasmon resonance properties, reaction time and nano-Au morphology. These Qi-related features on their own do not form sufficiently distinct clusters that are useful for the classification of the Qi-properties. The power of differentiation, however, is significantly improved when all the Qi-related features are considered together. The statistics of differentiation is encouraging, enabling us to develop a scheme which can classify all of the tested TCHMs into their respective Qi families. While this classification method was developed using a limited number of herbal medicines with known Qi properties, it has the potential to be applied as a scientific quick test to determine the Qi of new herbal medicines or herbal concoctions. It is our aspiration that this study can generate more interest in the development of non-reductionist approaches to modernize the understanding of TCHMs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...