Collagen structure regulates MSCs behavior by MMPs involved cell–matrix interactions
Abstract
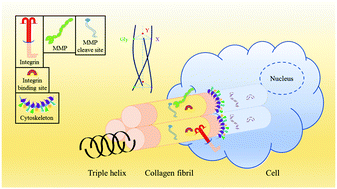
Various scaffolds have been studied in the formation of cell niches and regulation of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) behaviors. Collagen serves as one of the most promising materials for tissue engineering, but the cell–matrix interactions between MSCs and collagen are still poorly understood. In this study, we prepared methacrylated collagen (CMA) and gelatin (GMA) to form photo cross-linking hydrogels. The structure, morphology, mechanical properties and degradation behaviors of the derivatives and hydrogels were characterized and it was found that the advanced structure was the major difference between collagen and gelatin hydrogels. MSCs were encapsulated in the hydrogels and cultured for 14 days in vitro, with or without the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase (TIMP). The CCK-8 and CLSM demonstrated that the cells in the CMA hydrogels showed better spreading and proliferation than those in GMA hydrogels. The qRT-PCR and quantitative protein assay verified the inhibition effect of TIMP on metalloproteinases (MMPs). Since the inhibited MMPs led to inferior MSCs adhesion and proliferation, we considered that the appropriate degradation by MMPs would generate more bioactive domains and improve the cell microenvironment. Immunofluorescence staining further proved that the distribution of vitronectin was significantly related to MMP-1 and MMP-2. It was concluded that the differences in the advanced structures of the scaffold materials were amplified to significant differences in multiple biological cell–matrix interactions, and finally led to different cellular fates.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...