Controlled synthesis of Pt nanoparticle supported TiO2 nanorods as efficient and stable electrocatalysts for the oxygen reduction reaction†
Abstract
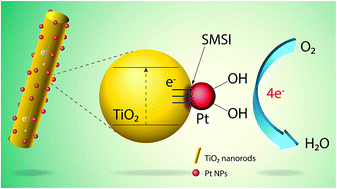
The development of adequate cathode materials is one of the principal tasks for the fabrication of efficient proton-exchange membrane fuel cells (PEMFCs), which are envisaged as clean energy sources for future transport and portable electrodomestic applications. Here, we present a platinum nanoparticle (NPs)-decorated one-dimensional (1D) titanium dioxide nanorod (PtNPs/TiO2NRs) nanocomposite with enhanced electrocatalytic performance towards the oxygen reduction reaction (ORR). The TiO2NRs were prepared through a green approach, utilizing seaweed extract that not only acts as a reducing agent but also serves as a soft template for the directional growth of TiO2 nanostructures. PtNPs of about 3.0 nm average size were decorated over pre-synthesized TiO2NRs through the chemical reduction of Pt ions using sodium borohydride. Scanning electron microscopy (SEM), transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray diffraction (XRD), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS), and Raman spectroscopy analyses confirmed the presence of strong metal-support interactions (SMSI) in the prepared hybrid nanocomposite. The as-prepared PtNPs/TiO2NRs composite nanostructures exhibited significantly enhanced electrocatalytic performance and stability towards the ORR, with specific and mass activities of 0.428 mA cm−2 at 0.55 V and 128 mA mg−1 Pt, respectively. These values are 7.2 and 3.5 fold higher than that of standard Pt/C catalysts (0.059 mA cm−2 and 36 mA mg−1 Pt), respectively. The enhanced catalytic activity and high stability of the composite catalyst are mainly due to the unique 1D morphology of the TiO2 nanostructures, which provides a greater surface area, and the SMSI enhancing electron transfer rate at their functional interface. The green approach utilized to fabricate the Pt/TiO2NRs composite in the present study provides a new, low-cost strategy for the development of metal–oxide hybrid nanostructures of high electrocatalytic activity for fuel cell applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...