Enabling efficient visible light photocatalytic water splitting over SrTaO2N by incorporating Sr in its B site†
Abstract
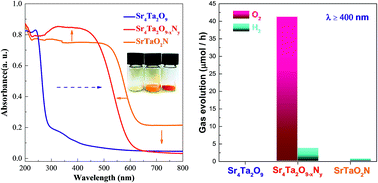
The perovskite oxynitride SrTaO2N is a promising compound for solar energy conversion because it has strong visible light absorption at wavelengths as long as 650 nm. However, its photocatalytic activity is generally very poor, primarily because of the high defect concentration induced during its synthetic procedures as well as photocatalytic self-decomposition events. In this work, we introduce Sr into the B site of SrTaO2N to form a complex perovskite oxynitride, Sr3(Sr1/3Ta2/3)3O9−xNy (i.e. Sr4Ta2O9−xNy). The new compound has a much lower defect concentration compared to SrTaO2N and much higher stability against photocatalytic self-decomposition. More importantly, Sr4Ta2O9−xNy demonstrates significantly improved photocatalytic activity for water oxidation and reduction reactions under visible light irradiation (λ ≥ 400 nm) than SrTaO2N, approaching an apparent quantum efficiency as high as 3.4% at 420 ± 20 nm.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...