Investigation of real polarization resistance for electrode performance in proton-conducting electrolysis cells†
Abstract
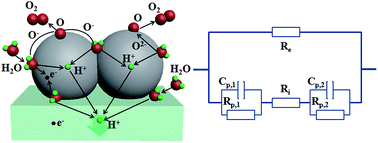
There has been great interest in proton-conducting electrolysis cells (PCECs) because they can effectively convert electric energy into chemical energy, and they possess unique advantages when compared to conventional cells that utilize oxygen ion-conducting electrolytes. However, the electronic leakage of Ce-doped BaZrO3 electrolytes becomes aggravated at enhanced applied electrolysis voltages, largely hinders the development of PCECs, and also conceals the intrinsic electrode performance. In this work, an R–P structure oxide, Sr2.8La0.2Fe2O7−δ (SLF), is proposed as a novel anode to investigate the electrode performance of PCECs. Good electrochemical performance of PCECs using an SLF anode is demonstrated. Operating at 1.30 V and 20% H2O–air, the electrolysis current densities are 1.08 and 0.46 A cm−2 at 700 and 600 °C, respectively. In addition, a button cell experienced a 30 hour short-term stability test under an electrolysis current of 0.21 A cm−2 without obvious degradation. To evaluate the intrinsic electrode performance, an equivalent circuit, which takes into account the electronic conduction in electrolyte, was proposed to analyse the impedance spectra of a practical PCEC measured at different electrolysis voltages and water vapour pressures (pH2O). Real polarization resistances hiding behind the electronic conduction were calculated using the above equivalent circuit. Intensive examination of the dependence of real polarization resistances on electrolysis voltages and pH2O suggest that in addition to electronic conduction in electrolytes, the different electrode reaction steps should account for the large reduced polarization resistance obtained in electrolysis mode compared with those in open circuit voltages (OCVs). Our work may provide new data regarding the investigation of intrinsic electrode performance in electrolysis cells.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...