Sn4P3–C nanospheres as high capacitive and ultra-stable anodes for sodium ion and lithium ion batteries†
Abstract
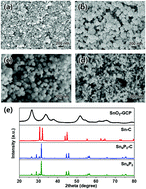
Tin phosphide (Sn4P3) has emerged as an anode for sodium ion batteries (SIBs) due to its high reversible capacity and low redox potential. Sn4P3 shows a synergistic Na-storage reaction to form Na15Sn4 and Na3P, but suffers from large volume expansion and Sn aggregation during the Na+ insertion–extraction resulting in poor cycle stability. Sn4P3 has also been considered a promising anode material for lithium ion batteries (LIBs), but very limited studies have been performed. Herein, core–shell Sn4P3–C (carbon) composite nanospheres are fabricated by carbonization/reduction and phosphorization of SnO2–GCP (glucose-derived, carbon-rich polysaccharide) nanospheres. The size of Sn4P3–C nanospheres is controlled to optimize their electrochemical performance as long-term stable anodes for SIBs and LIBs. Among them, the 140 nm-sized Sn4P3–C nanosphere electrode exhibits high reversible capacity, high rate capability, and ultra-long cycle stability as an anode for both SIBs and LIBs, delivering a high capacity of 420 mA h g−1 after 2000 cycles (SIBs) and 440 mA h g−1 after 500 cycles (LIBs) at a high current density of 2000 mA g−1. Hence, the Sn4P3–C nanospheres can be considered as a promising anode material for next generation SIBs and LIBs.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...