Silk-based systems for highly efficient photothermal conversion under one sun: portability, flexibility, and durability†
Abstract
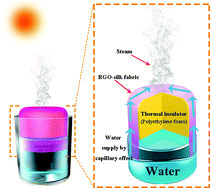
As one of the most promising techniques for harvesting solar energy, solar-powered generation of steam has great potential for application in sterilization, desalination, and other industrial processes. Although various methods of solar-powered steam generation have been reported, it remains a challenge to develop solar steam generators with durability, portability, and high photothermal performance for practical use. In this study, a novel device composed of reduced graphene oxide and silk fabric (RGO–silk-fabric) was demonstrated for highly efficient, solar-driven generation of steam. The unique fabric structure of silk and the broadband absorption by RGO allowed the RGO–silk-fabric to exhibit high light absorption in the wavelength range of 300 to 2500 nm. Benefitting from the capillary effect and superb air permeability, the RGO–silk-fabric system with a thermal insulator (polyethylene foam) exhibited remarkably high photothermal performances (an evaporation rate of 1.48 kg m−2 h−1) under one sun irradiation (1 kW m−2), even with minimal RGO content. Moreover, the RGO–silk-fabric showed great washability, flexibility, and excellent mechanical strength for low-cost, durable, and portable solar-steam applications. The simple fabrication process and scalability of the RGO–silk-fabric are expected to promote widespread application of the approach in water purification and other industrial processes.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...