N, P, S co-doped hollow carbon polyhedra derived from MOF-based core–shell nanocomposites for capacitive deionization†
Abstract
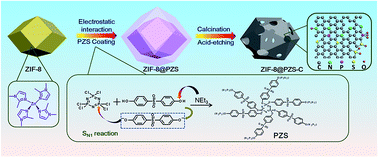
Capacitive deionization (CDI) is a prospective technique for desalination of saline water on account of its lower cost, lower energy-consumption, and absence of secondary pollution. In this work, capacitive deionization of saline water using N, P, S co-doped hollow carbon polyhedra derived from MOF-based core–shell nanocomposites has been demonstrated. N, P, S co-doped hollow carbon polyhedra were rationally designed and originally synthesized from MOF-based core–shell nanocomposites by using poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) coated zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 (denoted as ZIF-8@PZS-C). Choosing poly(cyclotriphosphazene-co-4,4′-sulfonyldiphenol) as an N, P, S co-doping source and carbon source, and ZIF-8 as a structural template which also acts as an additional N-doping source, ZIF-8@PZS-C was created with a superior hollow structure, high surface area, improved electrical conductivity and an excellent hydrophilic surface. Due to the multi-synergy of these characteristics, the ZIF-8@PZS-C electrodes have lower internal impedance, larger specific capacitance and great cycling stability. What's more, the ZIF-8@PZS-C electrodes display a high salt electrosorption performance of 22.19 mg g−1 at 1.2 V in a NaCl solution of 500 mg L−1. Furthermore, the as-prepared electrodes exhibit good stability and regeneration performance. Hence, the N, P, S co-doped hollow carbon polyhedra should be considered as a promising alternative electrode material for capacitive deionization. This work may open the door for the application of multiple heteroatom co-doped hollow carbon materials for the deionization of saline water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...