Thermal stability and miscibility of co-evaporated methyl ammonium lead halide (MAPbX3, X = I, Br, Cl) thin films analysed by in situ X-ray diffraction†
Abstract
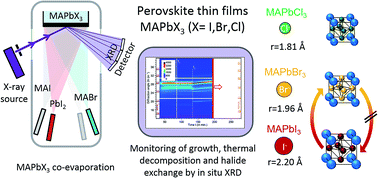
We present the identification of crystalline phases by in situ X-ray diffraction during growth and monitor the phase evolution during subsequent thermal treatment of CH3NH3PbX3 (X = I, Br, Cl) perovskite thin films. The thin films are prepared by vacuum-based two-source co-evaporation using various methyl ammonium (MA) halide and lead halide (PbX2) precursors. The single halide perovskite materials MAPbI3, MAPbBr3 and MAPbCl3 are prepared without secondary phases and an upper thermal limit for decomposition into the corresponding lead halides is established. We show that at a substrate temperature of 120 °C, the halide in MAPbI3/MAPbBr3 thin films can be completely and reversibly exchanged upon exposure to the opposite MA halide. We monitor the temporal evolution of the conversion process in situ and discuss differences in the forward and backward conversion. For the deposition of mixed MAPb(I,Br)3 perovskite thin films, different growth routes are suggested and evaluated in terms of growth with single phases or phase segregations. Our results are discussed in a broader context considering I/Br miscibility. Finally we propose a new growth route for the synthesizes of single phase mixed MAPb(I1−xBrx)3 thin films in the range from x = 0.3 to 1 by two source co-evaporation and discuss the implication of our results.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...