Radiation-induced grafting of a butyl-spacer styrenic monomer onto ETFE: the synthesis of the most alkali stable radiation-grafted anion-exchange membrane to date†
Abstract
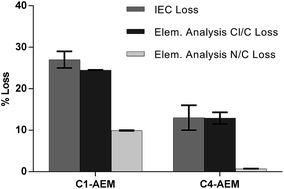
An ETFE-(poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene))-based radiation-grafted anion-exchange membrane (AEM) containing a butyl-spacer between the benzene and the methylpyrrolidinium groups (C4-AEM) had double the ex situ alkali stability at 80 °C compared to a methylene benchmark (C1-AEM). H2/O2 fuel cells containing C4-AEM still achieved a peak power density of >1 W cm−2.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...