Hydrophobicity of surface-immobilised molecules influences architectures formed via interfacial self-assembly of nucleoside-based gelators†
Abstract
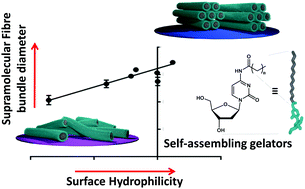
Surface-mediated self-assembly has potential in biomaterial development but underlying rules governing surface–gelator interactions are poorly understood. Here, we correlate surface properties with structural characterization data of nucleoside-based gels obtained by GISAXS and GIWAXS and find that hydrophobicity descriptors (log P, polar surface area, aromaticity) are key predictors for the gel structures formed.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...