Size effects in plasma-enhanced nano-transfer adhesion†
Abstract
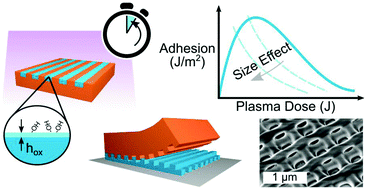
Plasma bonding and layer-by-layer transfer molding have co-existed for decades, and here we offer a combination of the two that drives both techniques to the nanoscale. Using fluorinated elastomeric stamps, lines of plasma-treated poly(dimethylsiloxane) (PDMS) were stacked into multi-layer woodpile structures via transfer molding, and we observe a pronounced size effect wherein nanoscale lines (≤280 nm period) require ultra-low plasma dose (<20 J) and fail to bond at the much higher range of plasma dose (600 J to 900 J) recommended in the PDMS plasma bonding literature. The size effect appears to be related to the thickness of the oxide film that develops on the PDMS surface during treatment, and we employ an empirical relationship, 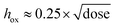 , to estimate the thickness of this film in the low plasma dose (<100 J) regime. The empirical relationship shows good agreement with existing studies on plasma-treated PDMS oxide film thickness, and the transition between successful transfer and delamination coincides well with a critical value of the oxide thickness relative to the thickness of the transferred layer. Through peel testing, we identified a transition in failure mode of flat plasma-bonded PDMS consistent with the optimal plasma dose in previous literature but otherwise observed strong, irreversible adhesion even at ultra-low plasma dose. By demonstrating the importance of low plasma dose for plasma-enhanced nano-transfer adhesion, these results advance our understanding of irreversible adhesion of soft materials at the nanoscale and open up new opportunities within the relatively unstudied ultra-low dose plasma treatment regime.
, to estimate the thickness of this film in the low plasma dose (<100 J) regime. The empirical relationship shows good agreement with existing studies on plasma-treated PDMS oxide film thickness, and the transition between successful transfer and delamination coincides well with a critical value of the oxide thickness relative to the thickness of the transferred layer. Through peel testing, we identified a transition in failure mode of flat plasma-bonded PDMS consistent with the optimal plasma dose in previous literature but otherwise observed strong, irreversible adhesion even at ultra-low plasma dose. By demonstrating the importance of low plasma dose for plasma-enhanced nano-transfer adhesion, these results advance our understanding of irreversible adhesion of soft materials at the nanoscale and open up new opportunities within the relatively unstudied ultra-low dose plasma treatment regime.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...
