Reverse relationships of water uptake and alkaline durability with hydrophilicity of imidazolium-based grafted anion-exchange membranes†
Abstract
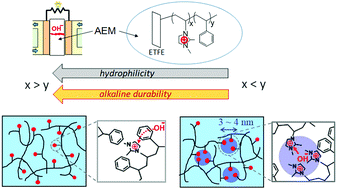
We found unprecedented reverse relationships in anion-exchange membranes (AEMs) for Pt-free alkaline fuel cell systems, i.e., the increase in hydrophobicity increased water uptake and susceptibility to hydrolysis. AEMs with graft copolymers that composed of anion-conducting 2-methyl-N-vinylimidazolium (Im) and hydrophobic styrene (St) units were employed. We characterized two new structures in these AEMs using a small-angle neutron scattering with a contrast variation method. (1) The distribution of graft polymers in conducting (ion channel) or non-conducting (hydrophobic amorphous poly(ethylene-co-tetrafluoroethylene) (ETFE)) phase was evaluated in a quantitative manner. High fraction in conducting layer for AEMs having high grafting degrees was found using the proposed structural model of “conducting/non-conducting two-phase system”. (2) Assuming a hard-sphere fluid model, we found AEMs having high St contents and low alkaline durability possessed nanophase-separated water puddles with diameters of 3–4 nm. The AEM having a low St content and the best alkaline durability did not show evident nanophase separation. The above hierarchical structures elucidate the unexpected reverse relationships that the AEM having highly hydrophobic graft polymers was subjected to the morphological transition to give water puddles at nanoscale. The imidazolium groups that were located at the boundary between graft polymers and water puddles should be susceptible to hydrolysis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...