Wall friction and Janssen effect in the solidification of suspensions
Abstract
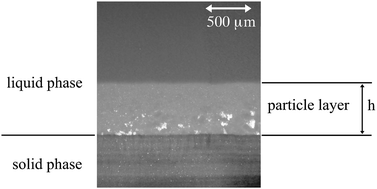
We address the mechanical effect of rigid boundaries on freezing suspensions. For this we perform the directional solidification of monodispersed suspensions in thin samples and we document the thickness h of the dense particle layer that builds up at the solidification front. We evidence a change of regime in the evolution of h with the solidification velocity V with, at large velocity, an inverse proportionality and, at low velocity, a much weaker trend. By modelling the force balance in the critical state for particle trapping and the dissipation phenomena in the whole layer, we link the former evolution to viscous dissipation and the latter evolution to solid friction at the rigid sample plates. Solid friction is shown to induce an analog of the Janssen effect on the whole layer. We determine its dependence on the friction coefficient between particles and plates, on the Janssen's redirection coefficient in the particle layer, and on the sample depth. Fits of the resulting relationship to data confirm its relevance at all sample depths and provide quantitative determinations of the main parameters, especially the Janssen's characteristic length and the transition thickness h between the above regimes. Altogether, this study thus clarifies the mechanical implication of boundaries on freezing suspensions and, on a general viewpoint, provides a bridge between the issues of freezing suspensions and of granular materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...