Characterization and differentiation of the adsorption behavior of crystal violet and methylene blue at the silica/water interface using near field evanescent wave
Abstract
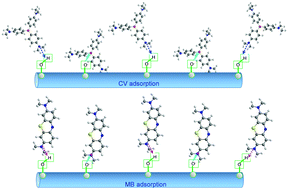
Different molecular structures lead to different adsorption performances. In this work, the adsorption behavior of two organic dyes, namely, crystal violet (CV, triphenylmethane dye of symmetric structure) and methylene blue (MB, azo dye of linear structure), were investigated, characterized and differentiated at the silica/water interface using the total internal reflection induced near field evanescent wave (TIR-NFEW) platform. According to the change in the evanescent wave intensity and following Beer's law, the adsorption behaviors of CV and MB can be monitored real time and sensitively. On one hand, the Langmuir adsorption model was applied to obtain the related thermodynamic data (including adsorption equilibrium constant (Kads) and adsorption free energy (ΔG)). With ΔG(MB) = −25.7 ± 1.7 kJ mol−1 < ΔG(CV) = −21.5 ± 0.6 kJ mol−1 < 0, the linear MB showed a higher spontaneous adsorption ability than the symmetric CV at the silica/water interface. On the other hand, a two-step adsorption kinetic model was applied to obtain the dynamics data including the linear adsorption rate constant (k1) and the exponential adsorption rate constant (k2). With k1(CV) < k1(MB) and k2(CV) ≈ k2(MB), MB diffused faster than CV at the first diffusion step but had nearly the same interaction speed as CV in the second adsorption step. A molecular-aligned-mechanism was successfully proposed to describe the interfacial interaction process for both CV and MB that includes molecular reactions involving electrostatic attraction of type I SiO− and H-bonds of type II SiOH. This work provides new insights into the molecular-level interpretation of the adsorption of the azo and triphenylmethane dyes at the silica–water interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...