Controlling deformations of gel-based composites by electromagnetic signals within the GHz frequency range†
Abstract
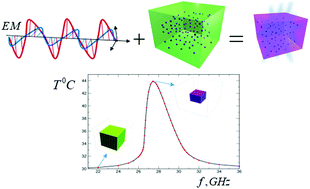
Using theoretical and computational modeling, we focus on dynamics of gels filled with uniformly dispersed ferromagnetic nanoparticles subjected to electromagnetic (EM) irradiation within the GHz frequency range. As a polymer matrix, we choose poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) gel, which has a low critical solution temperature and shrinks upon heating. When these composites are irradiated with a frequency close to the Ferro-Magnetic Resonance (FMR) frequency, the heating rate increases dramatically. The energy dissipation of EM signals within the magnetic nanoparticles results in the heating of the gel matrix. We show that the EM signal causes volume phase transitions, leading to large deformations of the sample for a range of system parameters. We propose a model that accounts for the dynamic coupling between the elastodynamics of the polymer gel and the FMR heating of magnetic nanoparticles. This coupling is nonlinear: when the system is heated, the gel shrinks during the volume phase transition, and the particle concentration increases, which in turn results in an increase of the heating rates as long as the concentration of nanoparticles does not exceed a critical value. We show that the system exhibits high selectivity to the frequency of the incident EM signal and can result in a large mechanical feedback in response to a small change in the applied signal. These results suggest the design of a new class of soft active gel-based materials remotely controlled by low power EM signals within the GHz frequency range.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...