Segregation of polymers under cylindrical confinement: effects of polymer topology and crowding†
Abstract
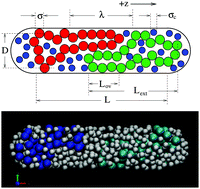
Monte Carlo computer simulations are used to study the segregation behaviour of two polymers under cylindrical confinement. Using a multiple-histogram method, the conformational free energy, F, of the polymers was measured as a function of the centre-of-mass separation distance, λ. We examined the scaling of the free energy functions with the polymer length, the length and diameter of the confining cylinder, the polymer topology (i.e. linear vs. ring polymers), and the packing fraction and size of mobile crowding agents. In the absence of crowders, the observed scaling of F(λ) is similar to that predicted using a simple model employing the de Gennes blob model and the approximation that the free energy of overlapping chains in a tube is equal to that of two isolated chains each in a tube of half the cross-sectional area. Simulations were used to test the latter approximation and reveal that it yields poor quantitative predictions. This, along with generic finite-size effects, likely gives rise to the discrepancies between the predicted and measured values of scaling exponents for F(λ). For segregation in the presence of crowding agents, the free energy barrier generally decreases with increasing crowder packing fraction, thus reducing the entropic forces driving segregation. However, for fixed packing fraction, the barrier increases as the crowder/monomer size ratio decreases.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...