Convection inside condensing and evaporating droplets of aqueous solution†
Abstract
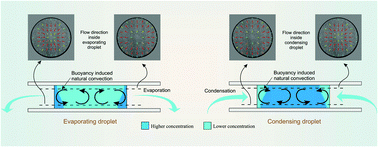
We experimentally study the fluid convection inside a condensing droplet of aqueous NaCl solution and compare it with that of an evaporating droplet. The droplets are sandwiched between two horizontal hydrophobic surfaces and surrounded by a reservoir with solution of different concentration. Condensation and evaporation of the droplets occur due to the vapor pressure difference between the droplet and the reservoir solution. The micro-PIV technique has been used to study the velocity field inside the droplets. Buoyancy driven Rayleigh convection is observed inside both the condensing and evaporating droplets. In the condensing droplet, water condenses on the liquid–air interface creating a low density region near the interface. There is upward movement of fluid along the condensing interface towards the top region of the droplet which recirculates back from the center region of the droplet in the downward direction. In contrast, the fluid moves in the downward direction along the interface in the case of an evaporating droplet with an upward plume like flow at the center region of the droplet. Both evaporating and condensing droplets show a recirculating loop inside the droplets of opposite direction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...