Stable emulsions of droplets in a solid edible organogel matrix
Abstract
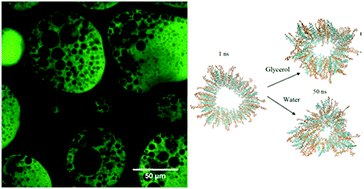
Sitosterol and oryzanol self-assemble to form very firm gels in a range of organic solvents. However, due to the formation of sitosterol hydrate crystals, these gels are unstable in the presence of water, prohibiting the dispersal of water droplets throughout the gel matrix. We demonstrate that by using glycerol as the polar phase rather than water, droplets may be dispersed throughout the oil phase without disrupting the self-assembly of the gel. As increasing volumes of water are added to the glycerol, the G′ values decrease. This can be correlated to both a drop in water activity, and also the stability of the fibrils in the presence of glycerol compared to water, as elucidated by molecular dynamics simulations. We explore how changing the total volume of polar droplets, and changing the water content of these droplets alters the strength of 15% w/w sterol gels. We find that gels exhibit G′ values of ∼1 × 107 Pa even with ∼30% w/w glycerol dispersed throughout the matrix. At higher glycerol loadings, complex multiple emulsion morphologies can form.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...