Adsorption of phospholipids at oil/water interfaces during emulsification is controlled by stress relaxation and diffusion
Abstract
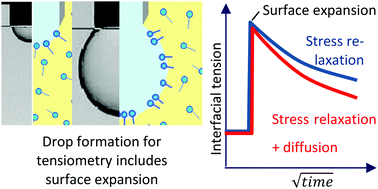
Adsorption of phosphatidylcholines at oil/water interfaces strongly deviates from spread monolayers at air/water surfaces. Understanding its nature and consequences could vastly improve applications in medical nanoemulsions and biotechnologies. Adsorption kinetics at interfaces of water with different oil phases were measured by profile analysis tensiometry. Adsorption kinetics for 2 different phospholipids, DPPC and POPC, as well as 2 organic phases, squalene and squalane, show that formation of interfacial monolayers is initially dominated by stress-relaxation in the first minutes. Diffusion only gradually contributes to a decrease in interfacial tension at later stages of time and higher film pressures. The results can be applied for the optimization of emulsification protocols using mechanical treatments. Emulsions using phospholipids with unsaturated fatty acids are dominated much more strongly by stress-relaxation and cover interfaces very fast compared to those with saturated fatty acids. In contrast, phospholipid layers consisting of saturated fatty acids converge faster towards the equilibrium than those with unsaturated fatty acids.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...