A cobalt hydroxide-based compressible electrode material for asymmetrical all-solid supercapacitors†
Abstract
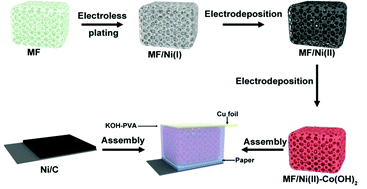
A compressible supercapacitor is a promising energy storage device for wearable flexible electronic devices. In this study, a compressible electrode material of MF/Ni(II)–Co(OH)2 based on melamine foam (MF) for all-solid supercapacitors was fabricated by an electroless plating and electrodeposition method. The electrode of MF/Ni(I) was prepared by electroless plating on commercial MF, and the subsequent step of electrodeposition was introduced to fabricate MF/Ni(II) and MF/Ni(II)–Co(OH)2. The electrochemical results show that the obtained compressible electrode material exhibits exceptional capacitive behavior (volumetric capacitance of 8.82 F cm−3 at 3 mA cm−3), cycling stability (80.95% capacitance retention after 1000 cycles at 10 mA cm−3), and superior compression stability (93.81% capacitance retention even under 50% compression). Then, a compressible asymmetrical all-solid supercapacitor was fabricated with MF/Ni(II)–Co(OH)2 as the positive electrode and Ni/carbon (Ni/C) as the negative electrode, separated by laboratory filter paper and KOH–poly(vinyl alcohol) (PVA) electrolyte. Such a compressible supercapacitor displays good capacitive behavior, exceptional compression stability (84.21% capacitance retention even under 50% compression) and cycling stability (94.44% capacitance retention after 1000 cycles at 10 mA cm−3). It has been shown that the assembled compressible supercapacitor can be used as a power source to drive a light-emitting diode (LED) and it can work properly under different compression conditions. These favorable results demonstrate that MF/Ni(II)–Co(OH)2 is an appropriate electrode material for compressible supercapacitors.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...