A bio-inspired approach to ligand design: folding single-chain peptoids to chelate a multimetallic cluster†
Abstract
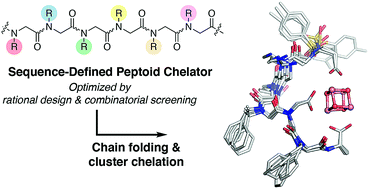
Synthesis of biomimetic multimetallic clusters is sought after for applications such as efficient storage of solar energy and utilization of greenhouse gases. However, synthetic efforts are hampered by a dearth of ligands that are developed for multimetallic clusters due to current limitations in rational design and organic synthesis. Peptoids, a synthetic sequence-defined oligomer, enable a biomimetic strategy to rapidly synthesize and optimize large, multifunctional ligands by structural design and combinatorial screening. Here we discover peptoid oligomers (≤7 residues) that fold into a single conformation to provide unprecedented tetra- and hexadentate chelation by carboxylates to a [Co4O4] cubane cluster. The structures of peptoid-bound cubanes were determined by 2D NMR spectroscopy, and their structures reveal key steric and side-chain-to-main chain interactions that work in concert to rigidify the peptoid ligand. This efficient ligand design strategy holds promise for creating new scaffolds for the abiotic synthesis and manipulation of multimetallic clusters.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 Chemical Science HOT Article Collection


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...