Dynamic tungsten diselenide nanomaterials: supramolecular assembly-induced structural transition over exfoliated two-dimensional nanosheets†
Abstract
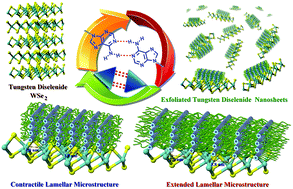
A simple and effective method for direct exfoliation of tungsten diselenide (WSe2) into few-layered nanosheets has been successfully developed by employing a low molecular weight adenine-functionalized supramolecular polymer (A-PPG). In this study, we discover A-PPG can self-assemble into a long-range, ordered lamellar microstructure on the surface of WSe2 due to the efficient non-covalent interactions between A-PPG and WSe2. Morphological and light scattering studies confirmed the dynamic self-assembly behavior of A-PPG has the capacity to efficiently manipulate the transition between contractile and extended lamellar microstructures on the surface of metallic 1T-phase and semiconducting 2H-phase WSe2 nanosheets, respectively. The extent of WSe2 exfoliation can be easily controlled by systematically adjusting the amount of A-PPG in the composites, to obtain nanocomposites with the desired functional characteristics. In addition, the resulting composites possess unique liquid–solid phase transition behavior and excellent thermoreversible properties, revealing the self-assembled lamellar structure of A-PPG functions as a critical factor to manipulate and tailor the physical properties of exfoliated WSe2. This newly developed method of producing exfoliated WSe2 provides a useful conceptual and potential framework for developing WSe2-based multifunctional nanocomposites to extend their application in solution-processed semiconductor devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...