Protecting group free radical C–H trifluoromethylation of peptides†
Abstract
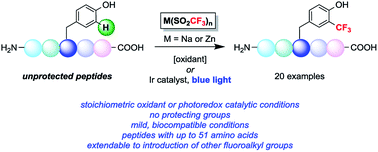
Two radical-based approaches have been developed to effect the trifluoromethylation of aryl C–H bonds in native peptides either using stoichiometric oxidant or visible light photoredox catalysis. The reported methods are able to derivatize tyrosine and tryptophan sidechains under biocompatible conditions, and a number of examples are reported involving fully unprotected peptides with up to 51 amino acids. The development of this chemistry adds to the growing array of chemical methods for selectively modifying amino acid residues in the context of complex peptides. The direct incorporation of trifluoromethyl groups into biopolymers enables the study of a range of biological and biochemical systems, and preliminary results indicate this method can be extended to the incorporation of other fluoroalkyl groups for bioconjugation applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...