Mononuclear complexes of a tridentate redox-active ligand with sulfonamido groups: structure, properties, and reactivity†
Abstract
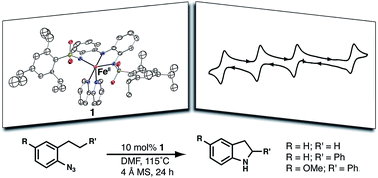
The design of molecular complexes of earth-abundant first-row transition metals that can catalyze multi-electron C–H bond activation processes is of interest for achieving efficient, low-cost syntheses of target molecules. To overcome the propensity of these metals to perform single-electron processes, redox-active ligands have been utilized to provide additional electron equivalents. Herein, we report the synthesis of a novel redox active ligand, [ibaps]3−, which binds to transition metals such as FeII and CoII in a meridional fashion through the three anionic nitrogen atoms and provides additional coordination sites for other ligands. In this study, the neutral bidentate ligand 2,2′-bipyridine (bpy) was used to complete the coordination spheres of the metal ions and form NEt4[MII(ibaps)bpy] (M = Fe (1) or Co (1-Co)) salts. The FeII salt exhibited rich electrochemical properties and could be chemically oxidized by 1 and 2 equiv. of ferrocenium to form singly and doubly oxidized species, respectively. The reactivity of 1 towards intramolecular C–H bond amination of aryl azides at benzylic and aliphatic carbon centers was explored, and moderate to good yields of the resulting indoline products were obtained.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...