On the intrinsic dynamic nature of the rigid UiO-66 metal–organic framework†
Abstract
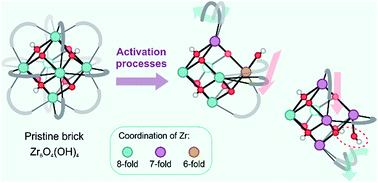
UiO-66 is a showcase example of an extremely stable metal–organic framework, which maintains its structural integrity during activation processes such as linker exchange and dehydration. The framework can even accommodate a substantial number of defects without compromising its stability. These observations point to an intrinsic dynamic flexibility of the framework, related to changes in the coordination number of the zirconium atoms. Herein we follow the dynamics of the framework in situ, by means of enhanced sampling molecular dynamics simulations such as umbrella sampling, during an activation process, where the coordination number of the bridging hydroxyl groups capped in the inorganic Zr6(μ3-O)4(μ3-OH)4 brick is reduced from three to one. Such a reduction in the coordination number occurs during the dehydration process and in other processes where defects are formed. We observe a remarkable fast response of the system upon structural changes of the hydroxyl group. Internal deformation modes are detected, which point to linker decoordination and recoordination. Detached linkers may be stabilized by hydrogen bonds with hydroxyl groups of the inorganic brick, which gives evidence for an intrinsic dynamic acidity even in the absence of protic guest molecules. Our observations yield a major step forward in the understanding on the molecular level of activation processes realized experimentally but that is hard to track on a purely experimental basis.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...