Continuous hydrothermal flow synthesis of graphene quantum dots†
Abstract
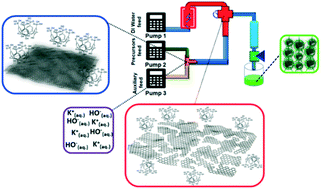
Green fluorescent graphene quantum dots (GQD) have been synthesized via hydrothermal fragmentation using a continuous hydrothermal flow synthesis (CHFS) process as a single, rapid and environmentally benign method. This is in the presence of p-phosphonic acid calix[4]arene which enhances the optical properties of the graphene quantum dots through surface functionalization, with photoluminescence quantum yields of up to 4.5%. Potential environmental impact of a lab-scale supercritical CHFS process compared with that of conventional batch processing of GQDs has been assessed using the method of the International Reference Life Cycle Data System (ILCD).


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...