Mechanistic insight into oxidized N,N-dimethylacetamide as a source of formaldehyde related derivatives†
Abstract
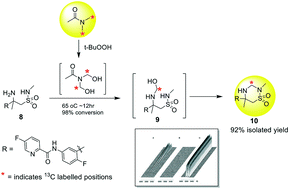
A hemiaminal derivative identified during preparation of the penultimate of ceftolozane 1, mandated a thorough investigation of the source of the impurity. N,N-Dimethylacetamide (DMAc) subjected to oxidation was found to be the culprit generating oxidized products that serve as sources of the hemiaminal derivative. Identification of DMAc as a source of formaldehyde derivatives and the mechanism of DMAc oxidation are elaborated.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...