Dropwise condensation on bioinspired hydrophilic-slippery surface
Abstract
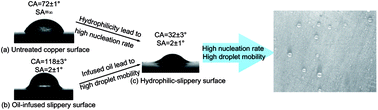
To promote the water vapor condensation efficiency in the presence of a non-condensable gas, both high nucleation rate and efficient droplet departure are desired on the condensing surface. Superhydrophobic surfaces with large water contact angles ensure the dropwise condensation mode and efficient droplet departure ability. Alternatively, efficient nucleation requires the surface to be hydrophilic. To combine these two seemingly contradictory factors on a single surface, we presented a copper-based hydrophilic-slippery surface in this study by depositing a lubricant (trimethoxysilane) on the microstructured copper substrate. The water droplet had both low contact angles and sliding angles on the surface, and stable dropwise condensation could be realized with and without non-condensable gas. The present hydrophilic-slippery surface demonstrated promising potential to enhance condensation heat transfer, particularly for cases with non-condensable gas. Improved droplet mobility was observed as compared to a superhydrophobic surface, hydrophobic surface, and hydrophobic-slippery surface. The most attractive feature lies in the enhanced nucleation process due to hydrophilicity, which is more favorable as it requires small subcooling degree and large non-condensable gas content. By revealing that a sliding angle could be accompanied by a small contact angle, this hydrophilic-slippery surface could improve our understanding in designing new functional surfaces for phase change, anti-icing, self-cleaning, and anti-fouling applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...