Analysis of effect of oil and S2− impurities on corrosion behavior of 16Mn steel for storage tanks by electrochemical method
Abstract
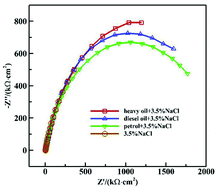
Corrosion is a common problem of storage tanks, and different storage media and impurities have different effects on the corrosion behavior of steel used for tanks. In this paper, electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) and polarization curves were used to study the corrosion behavior of 16Mn steel in 3.5% sodium chloride solution after immersion in heavy oil, diesel oil and gasoline, considering the influence of the main impurities, S2−, on the corrosion process. The results showed that the self-corrosion current density of 16Mn steel in the solution after the immersion in gasoline was higher than that in heavy oil and diesel oil, due to the higher dissolved oxygen concentration promoting the cathodic reaction. The comparison of blank sample in 3.5% sodium chloride solution and the immersed samples showed that the corrosion rate of the 16Mn steel decreased in the presence of an oil film on the surface of the steel. With the increase of S2− concentration in the oil, the corrosion rate of 16Mn steel tended to be stable after it gradually increased. This was mainly related to the composition of FeS and FeS1−x in the sulfide film formed on the surface of the steel as well as the change of the lattice structure.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...