NOx reduction by CO over ASC catalysts in a simulated rotary reactor: effect of CO2, H2O and SO2†
Abstract
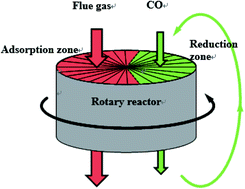
The influence of CO2, H2O and SO2 on the NO reduction by CO over Fe/Co activated semi-coke catalyst was investigated in a simulated rotary reactor. The results showed that, in the simulated rotary reactor, the influence of CO2 and H2O on the NO adsorption was significant at low temperatures, and the inhibition became weak when increasing the temperature. However, the NO adsorption efficiency could not be improved by increasing temperature after catalyst sulfur poisoning. The heavily inhibited NO adsorption process, which was due to the competitive adsorption and formation of the sulfate, resulted in a low NO reduction efficiency in the presence of CO2, H2O or SO2. The in situ DRIFT study showed that the dominant effect of CO2, H2O and SO2 on the NO adsorption was the inhibition of the free nitrate ions formation. In addition, the introduction of CO2, H2O and SO2 could not change the route of NO reduction, but just reduced the degree of the NO + CO reduction.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...