Rapid fabrication of porous silicon/carbon microtube composites as anode materials for lithium-ion batteries
Abstract
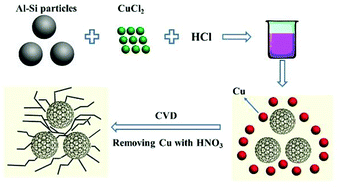
Herein, we present a simple and rapid method to synthesize porous silicon/carbon microtube composites (PoSi/CMTs) by adopting a unique configuration of acid etching solution. The CMTs can act as both conductive agent and buffer for Si volume change during the charge and discharge process. The highly reversible capacity and excellent rate capability can be ascribed to the structure, where porous silicon powders are wrapped by a network of interwoven carbon microtubes. The composites show specific capacities of more than 1712 mA h g−1 at a current density of 100 mA g−1, 1566 mA h g−1 at 200 mA g−1, 1407 mA h g−1 at 400 mA g−1, 1177 mA h g−1 at 800 mA g−1, 1107 mA h g−1 at 1000 mA g−1, 798 mA hg−1 at 2000 mA g−1, and 581 mA h g−1 at 3000 mA g−1 and maintain a value of 1127 mA h g−1 after 100 cycles at a current density of 200 mA g−1. Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) measurements prove that charge transfer resistance of PoSi/CMT composites is smaller than that of pure PoSi. In this study, we propose a quick, economical and feasible method to prepare silicon-based anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...