Photovoltaic and photocatalytic properties of bismuth oxyiodide–graphene nanocomposites†
Abstract
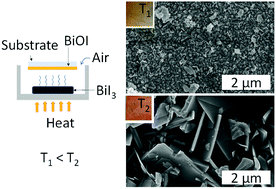
In this study, we evaluate the photovoltaic and photocatalytic properties of chemical vapor deposited bismuth oxyiodide (BiOI) and bismuth oxyiodide–graphene (BiOI–GR) nanocomposite thin films. The BiOI thin film has an average thickness of 574 nm and a bandgap of around 2 eV. The BiOI and BiOI–GR thin films exhibited nanoflake morphology. It was found that addition of graphene increases absorbance by causing vertical growth of nanoflakes, imparting anti-reflectance and light trapping properties. The photocatalytic activities of the thin films were evaluated by examining methylene blue (MB) degradation under visible light irradiation. BiOI–GR degraded 56.42% of MB in two hours while BiOI degraded 44.16%. Afterwards, FTO|BiOI|graphite|Al and FTO|BiOI–GR|graphite|Al solar cell devices were fabricated with photocurrent density values of 2.0 μA cm−2 and 2.7 μA cm−2, respectively. The improved properties of BiOI–GR are attributed to the anti-reflecting and light trapping properties of vertical BiOI–GR nanoflakes and the enhanced carrier separation due to graphene as an electron acceptor.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...