Co-production of fully renewable medium chain α-olefins and bio-oil via hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass containing polyhydroxyalkanoic acid
Abstract
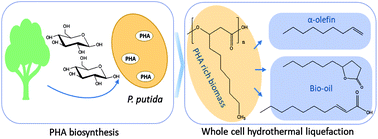
Medium chain-length linear α-olefins (mcl-LAO) are versatile precursors to commodity products such as synthetic lubricants and biodegradable detergents, and have been traditionally produced from ethylene oligomerization and Fischer–Tropsch synthesis. Medium chain-length polyhydroxyalkanoic acid (mcl-PHA) can be produced by some microorganisms as an energy storage. In this study, Pseudomonas putida biomass that contained mcl-PHA was used in HTL at 300 °C for 30 min, and up to 65 mol% of mcl-PHA was converted into mcl-LAO. The yield and quality of the bio-oil co-produced in the HTL was remarkably improved with the biomass rich in mcl-PHA. Experiments with extracted mcl-PHA revealed the degradation mechanism of mcl-PHA in HTL. Overall, this work demonstrates a novel process to co-produce mcl-LAO and bio-oil from renewable biomass.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...