Oxide removal and stabilization of bismuth thin films through chemically bound thiol layers†
Abstract
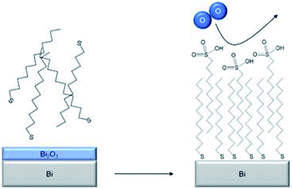
Bismuth has been identified as a material of interest for electronic applications due to its extremely high electron mobility and quantum confinement effects observed at nanoscale dimensions. However, it is also the case that Bi nanostructures are readily oxidised in ambient air, necessitating additional capping steps to prevent surface re-oxidation, thus limiting the processing potential of this material. This article describes an oxide removal and surface stabilization method performed on molecular beam epitaxy (MBE) grown bismuth thin-films using ambient air wet-chemistry. Alkanethiol molecules were used to dissolve the readily formed bismuth oxides through a catalytic reaction; the bare surface was then reacted with the free thiols to form an organic layer which showed resistance to complete reoxidation for up to 10 days.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...