Effects of proton conduction on dielectric properties of peptides†
Abstract
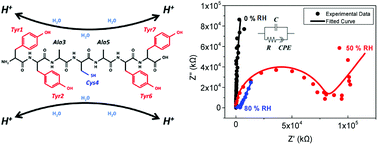
Peptides have been overlooked for their use in the field of electronics, even though they are one of the most commonly found bio-induced materials, and are not only easy to mass-produce but also exhibit a high dielectric constant. Additionally, unlike proteins, which are gaining considerable interest with materials researchers, peptides are much simpler, rendering their original characteristics easier to maintain without significant alteration of their structure. On the other hand, proteins tend to deform due to their susceptibility to environmental changes. Combining such superb dielectric properties with their relatively stable nature, peptides could be utilized as a component of electronic devices ranging from basic capacitors to more complex thin-film transistors. In this paper, a peptide chain (YYACAYY) composed of tyrosine, alanine, and cysteine was extensively studied using an impedance analyzer to determine its innate charge movement mechanism in order to extend our understanding of the electric properties of peptides. The movement of mobile protons inside the peptide insulator was found to be the source of the high relative permittivity of the peptide insulator, and the dielectric constant of the peptide insulator was found to be over 17 in humid conditions. By widening the understanding of the dielectric properties of the peptide insulator, it is expected that the peptide can be further utilized as an insulator in various electronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...